

Other causes for TOS are bony and soft tissue irregularities. The condition can be caused by an extra first rib or an old fracture of the collarbone that reduces the space for the vessels and nerves. TOS is named for the space between the lower neck and upper chest where the grouping of nerves and blood vessels can be found. Finally, a nerve conduction study may be recommended if there is the possibility of any nerve damage.BACKGROUND: Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) occurs when there is compression, injury, or irritation of the nerves or blood vessels in the lower neck and upper chest area. To check the blood vessels, either an angiography, arteriography or venography may be recommended. In order to confirm a diagnosis your doctor may recommend imaging tests such as x-rays, ultrasound or CT or MRI scans. You may be asked to move your arms, shoulders or neck into different positions to determine if any pain or other symptoms occur (this is called 'provocation testing'). Arterial pulse either absent or decreased on the affected side.Ī doctor will first review medical history and current symptoms and then conduct a physical examination to check for any of the symptoms listed above.One hand noticeably cooler than the other.
#Thoracic outlet syndrome armpit pain skin
Skin discolouration on the arm – either a bluish colour or paleness of the skin.Symptoms of vascular thoracic outlet syndrome may also include… Weakness, or a tingling or numbing of the arm or hand.Pain that worsens as the arm is lifted or during repetitive arm movements or when turning the head or neck.Pain in the arm – this can be in the form of an ache or a stabbing or burning pain.

Symptoms can be divided into those that occur in both type of the condition, and those that only occur with vascular thoracic outlet syndrome. Most symptoms of the condition affect the neck, the arms and hands and the shoulders and sometimes the chest and upper back. Pregnancy – joints and ligaments naturally loosen during pregnancy.Injury to the neck (especially whiplash in car accidents, but also consistently carrying around heavy bags or backpacks).stocking shelves, typing on a computer) or in certain sports, for example swimming, volleyball, golf and weightlifting. Overuse of the arms and/or shoulders - this is relatively common where heavy loads are frequently carried on the shoulders, or in jobs which require very repetitive movements of the arms (e.g.Congenital anatomical differences – a small number of people have an extra rib or particularly tight fibrous connective tissue in the area of the thoracic outlet which can place pressure on the nerves or blood vessels.The primary cause of the condition is injury or compression of the blood vessels and/or nerves in the thoracic outlet. It is unusual for the condition to develop under the age of 20 or over the age of 50. The condition (sometimes simply referred to as 'TOS') affects around 1% of the population, with women over twice as likely to develop it than men. Thoracic outlet syndrome describes where either the blood vessels (vascular thoracic outlet syndrome) or the nerves (neurological thoracic outlet syndrome) become injured, entrapped or compressed in the thoracic outlet.īy far the most common of these is neurological thoracic outlet syndrome. Nerves, arteries and veins pass through the thoracic outlet – specifically the nerves in the brachial plexus, the subclavian artery and the subclavian vein.
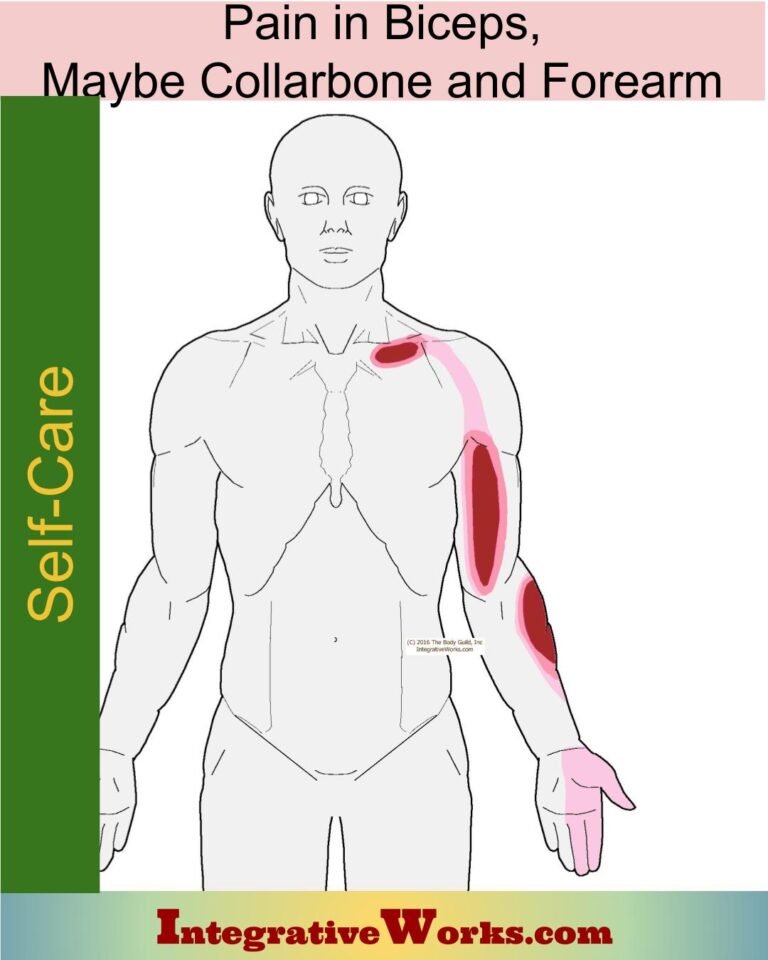
The thoracic outlet is a narrow passage located inside the body between the neck and the shoulder.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
